Ensuring Your Legal Rights
Strategic Criminal Defense Approach
Getting charged with a crime is often one of the most harrowing, stressful, and scary events a person can face in their life. A criminal conviction can have a long and far-reaching impact. It is imperative that you understand your rights and make an informed choice for who will be your voice in the courtroom. The following information is provided to help you better understand the criminal court process in North Carolina. We hope you will consider contacting our firm to assist you in your time of need.
Types of Criminal Charges
Generally speaking, criminal charges in North Carolina are broken into two main categories: Misdemeanors and Felonies. These are further divided into classes based on the severity of the crime and the prescribed punishment for each crime.
Misdemeanors
Misdemeanors are generally considered “low-level” offenses, but do not be misled; misdemeanors are serious business. A conviction for a misdemeanor will go on your criminal record and subject you to punishment as determined by a judge and North Carolina’s structured sentencing guidelines. Further, a criminal conviction can impact you outside of the court system. Many applications, from jobs to schooling to credit, will ask about prior criminal convictions.
Misdemeanors are classified from most serious (Class A1) to least serious (Class 3). What follows are some common misdemeanors, organized by class. Please note, this is not an exhaustive list of all misdemeanors in North Carolina. It will, however, give you an idea of how misdemeanor classes work.
Class A1 (most serious misdemeanors): Assault on a Government Official, Assault on a Female, Assault on a Handicapped Person, Assault on a Child under 12 years of age, Assault by Pointing a Gun, Sexual Battery, Child Abuse, Stalking, Violation of Domestic Violence Protective Order, Misdemeanor Death by Motor Vehicle, Interference with an Emergency Device
Class 1: Injury to Personal Property, Injury to Real Property, Armed to the Terror of the Public, False Imprisonment, Misdemeanor Breaking and Entering, Larceny (under $1,000), Secret Peeping, Communicating Threats, Contributing to the Delinquency of a Minor, Animal Cruelty, Carrying Concealed Weapon into Establishment Selling Alcohol, Sell/Give/Aid and Abet providing alcohol to underage person, Possession of Alcohol Under Age 19, Possession of Unspecified Controlled Substance, Possession of Marijuana above ½ ounce but less than 1 ½ ounce, Possession of Non-Marijuana Drug Paraphernalia
Class 2: Simple Assault, First Degree Trespass, Indecent Exposure, Carrying Concealed Weapon, Resist/Obstruct/Delay Public Officer, False Report to Law Enforcement, Disorderly Conduct, Impaired Instruction, Tampering with Motor Vehicle, Boating While Impaired, Drive After Consuming under 21 years of age, Cyberstalking
Class 3: Second Degree Trespass, Possession of Marijuana under ½ ounce, Concealment of Goods/Shoplifting, Trespass on Railroad Right of Way, Vandalism, Intoxicated and Disruptive in Public
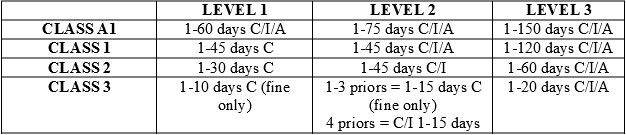
Misdemeanor punishment also depends on a Defendant’s prior conviction level. A prior record level one means no convictions on a person’s record. A prior record level two means one to four prior convictions on a person's record level. A prior record level three means five or more prior convictions on a person's record level. The class of offense and the Defendant’s prior record level determine the guidelines a judge must follow when sentencing the Defendant. The chart at the bottom of this page illustrates sentencing blocks.
Felonies
Historically, felonies were considered the most serious offenses and were punished accordingly. Felonies are still very serious and can have lifelong ramifications upon a conviction. One example is that felons cannot own or possess a firearm. Should you find yourself or a loved one facing a felony charge, it is important to be aggressive in your defense; don't delay! Call our office for a no-cost case analysis.
Felonies are classified from most serious (Class A) to least serious (Class I). What follows are some common felonies, organized by class. Again, please note, this is not an exhaustive list of all felonies in North Carolina. It will, however, give you an idea of how felony classes work.
Class A (most serious felony): First-Degree Murder
Class B1: Second-Degree Murder (malice but no premeditation and deliberation), First-Degree Forcible Rape, First-Degree Statutory Rape, First-Degree Forcible Sex Offense, First-Degree Statutory Sexual Offense
Class B2: Second-Degree Murder (no malice but inherently dangerous OR proximately caused by unlawful distribution of opioid)
Class C: Second-Degree Forcible Rape, First-Degree Kidnapping, Second-Degree Forcible Sexual Offense, Assault with a Deadly Weapon with Intent to Kill Inflicting Serious Injury, Embezzlement (over $100,000)
Class D: Voluntary Manslaughter, First-Degree Burglary, First-Degree Arson, Armed Robbery, Felony Death by Motor Vehicle, Child Abuse Inflicting Serious Physical Injury
Class E: Sexual Activity by a Substitute Parent/Custodian, Assault with a Deadly Weapon Inflicting Serious Injury, Assault with a Deadly Weapon with Intent to Kill, Discharge Weapon into Occupied Property, Assault on Government Official with Firearm, Second-Degree Kidnapping, Sell/Deliver Controlled Substance within 1000 feet of a school
Class F: Involuntary Manslaughter, Assault Inflicting Serious Bodily Injury, Assault with Deadly Weapon on Government Employee, Assault Inflicting Serious Bodily Injury on Law Enforcement Officer, Felonious Restraint, Indecent Liberties, Possession of Weapon of Mass Destruction, Habitual Impaired Driving
Class G: Second-Degree Burglary, Second-Degree Arson, Common Law Robbery, Identity Theft, Possession of Firearm by Felon, Sale Schedule I or II Controlled Substance
Class H: Felony Larceny, Felony Breaking and Entering, Assault by Strangulation, Habitual Misdemeanor Assault, Possession Stolen Goods, Obtain Property by False Pretense, Embezzlement (under $100,000), Possession with Intent to Sell/Manufacture/Deliver Cocaine, Sale of Schedule III, IV, V, VI Controlled Substance, Hit and Run causing bodily injury, Escape from jail/prison
Class I: Breaking or Entering Motor Vehicle, Financial Card Theft, Forgery, Possession with Intent to Sale/Manufacture/Deliver Marijuana, Possession Specified Controlled Substance, Felony Maintain Dwelling for Controlled Substances, Possession Marijuana greater than 1 ½ ounces
Felony punishment also depends on a Defendant's prior record level. Prior record level is determined by prior convictions. The higher the class level of prior conviction, the more points are assigned to a Defendant's prior record level. A person with no prior felony convictions or class A1 or 1 misdemeanor convictions would be a Felony Record Level 1, generally speaking.
Habitual Felon
A Defendant qualifies for Habitual Felon enhancement upon a conviction of a third felony if the prosecutor pursues a Habitual Felon indictment. If the Defendant is 1) convicted of the underlying Felony, and 2) is found to be a Habitual Felon beyond a reasonable doubt (or admits his/her status as a Habitual Felon), the punishment level for the underlying felony is increased by 4 classes up to a maximum of a Class C felony.
- Class I becomes a Class E
- Class H becomes a Class D
- Class D, E, F, G become a Class C
Special rules apply for the timing requirements of the underlying felony convictions for qualification as a habitual felon. Further, there are other sentence enhancements that could apply depending on the charge and the Defendant's background, such as violent habitual felon or habitual misdemeanors. Long story short, this stuff can be confusing and can make all the difference in sentencing, should the Defendant be convicted. The felony sentencing chart below helps illustrate the ranges of punishment for North Carolina felonies.
Punishment Categories
- No active sentence (see exception below)
- No assignment to drug court
- No special probation
- Supervised probation, unsupervised probation, or a fine only, are types of community punishment
- May receive community service, house arrest with electronic monitoring
- Could receive 2-3 days active in a local confinement facility; no more than 6 days per month during any three separate months
- Can be ordered to substance abuse assessment/treatment
- Can be ordered to vocational classes
- If a sex offender, can be ordered to satellite-based monitoring
- Any of Community Punishment conditions listed above
- Supervised probation
- One of the following specific conditions of probation
- Special probation
- Residential program
- Electronic house arrest
- Intensive probation
- Day reporting center
- Drug treatment court
- May be subjected to active incarceration up to ¼ of the suspended active sentence
- Active incarceration at either a local confinement facility (jail), through the Statewide Misdemeanant Confinement Program, or through the Division of Adult Corrections
- Where the sentence is served depends on nature of underlying offense and sentence received
Misdemeanor Punishment Grid
Felony Punishment Grid
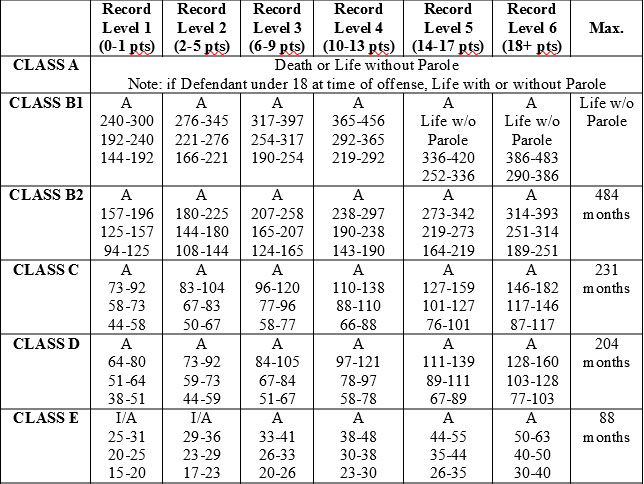
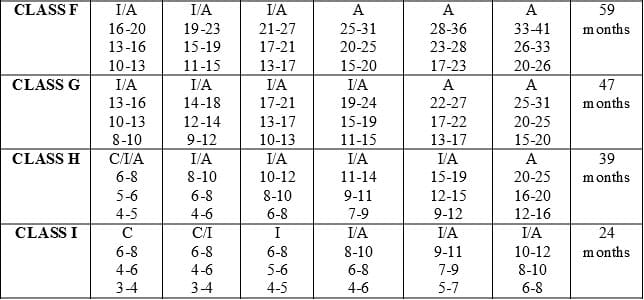
*Note: The numbers in the chart are the minimum number of months*
*Note: The top line is aggravated range, the middle line is presumptive range, and the bottom line is mitigated range - aggravating and mitigating factors listed by statute*
*Note: There are special sentencing rules for Sex Offenses and Trafficking Charges*